Material
ANDRITZ developed a water intake screen made of Cu/Ni 90/10 for usage in water bodies with a quagga or zebra mussel problem. This material has many advantages:
Quagga mussels are invasive mussels from the Black and Caspian Seas, now widespread in North American and European waters. Introduced to the Great Lakes in the 1980s, likely through ballast water, they quickly spread across the U.S. and Canada, impacting lakes, rivers, and reservoirs. Known for blocking water intake systems, quagga mussels increase maintenance costs and disrupt water treatment. Their high reproductive rate worsens these issues, while their plankton consumption harms native species and degrades water quality. Managing their spread and ecological impact is an ongoing challenge in both continents.
ANDRITZ teamed up with scientists to research the habitat and reproductive behavior of quagga mussels and found two limiting factors to eliminate the plugging of water intake screens by quagga mussels.
ANDRITZ developed a water intake screen made of Cu/Ni 90/10 for usage in water bodies with a quagga or zebra mussel problem. This material has many advantages:
Biofouling resistance
Quagga mussels typically attach to surfaces through byssal threads (protein-based filaments), and copper-based alloys make it difficult for them to successfully form these attachments. The leaching of copper from Cu/Ni materials can interfere with the mussels' ability to create a strong attachment bond, which prevents them from becoming established.
Long-term protection
The combination of copper and nickel enhances the corrosion resistance of the alloy, which also contributes to its longevity and effectiveness in preventing biofouling. Cu/Ni materials are durable in harsh water conditions (including freshwater and saltwater) and maintain their biocidal properties over time, making them a reliable solution for infrastructure exposed to mussel infestations.
Environmental considerations
Although copper is toxic to quagga mussels, the concentrations that leach from Cu/Ni alloys are typically low enough to be effective against mussels without causing significant harm to other aquatic life, though this can depend on the specific environment and the concentrations of copper in the water.
Contrary to regular water intake screens which use V-shaped wires, ANDRITZ developed a water intake system with round wires. Research showed that quagga and zebra mussels have a problem attaching to smooth and round surfaces. This smooth design minimizes the physical contact points that mussels can grip onto, preventing them from forming strong attachments.
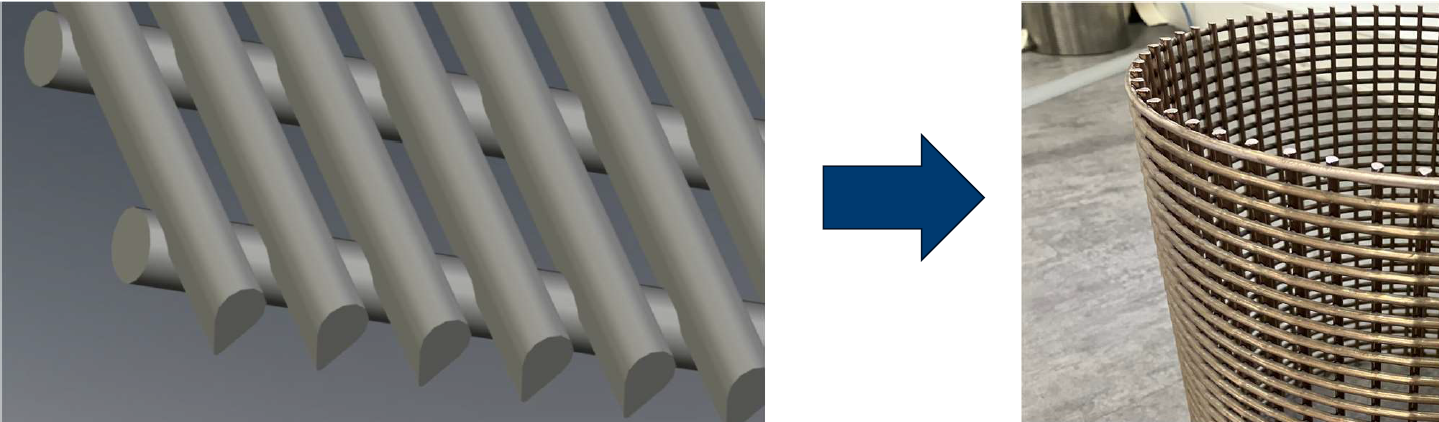
ANDRITZ water intake screen with round wires
Quagga mussel resistant material and design
Long-term protection
Maintenance free
Meets fish protection laws
No environmental damage to other species
Just complete this form and we will get back to you right away.
