Delivering the plants with performance guarantees
As a solution provider, we utilize proprietary technology, in-house core components and expert integration engineering, allowing us to offer performance guarantees for entire plants.
Methanol is one of the most widely used industrial chemicals today, with global production reaching over 100 million metric tons annually. Concurrently, more than 99% of methanol is produced using fossil fuels, accounting for about 1,8% of global CO₂ emissions. The world needs a more sustainable alternative.
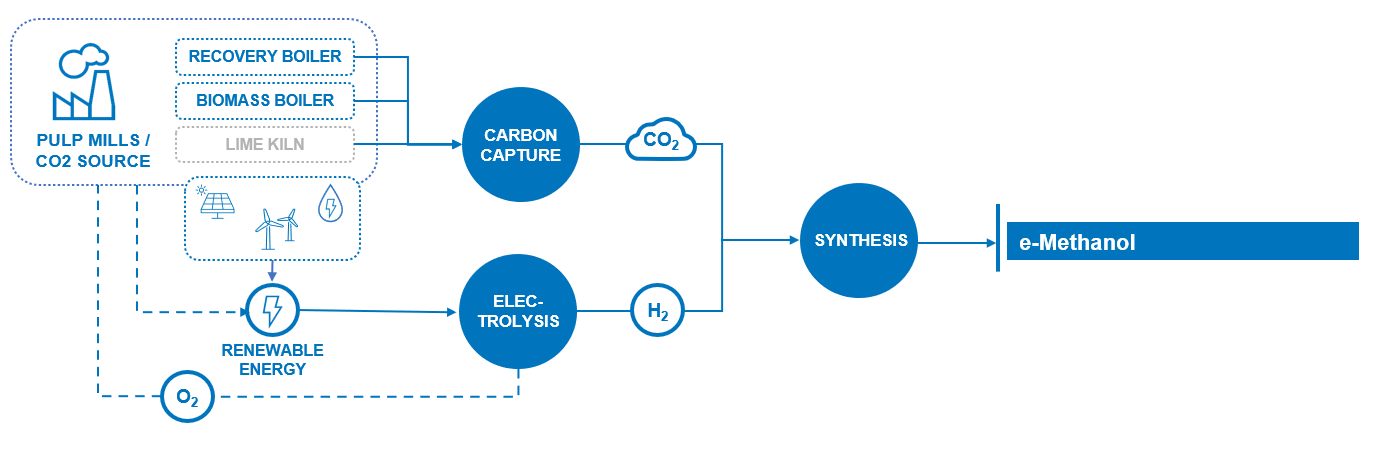
ANDRITZ provides holistic and integrated solutions for e-methanol production, formulated by converting carbon dioxide and green hydrogen. We deliver technology-focused, complete EPC (engineering, procurement, construction) solutions, including early engineering consulting services. Concurrently, we offer LTSA (long-term service agreements) for operation and maintenance. Our experts guide you through every step of the project — design, execution and operation. Our technologies provide the lowest levelized cost of e-methanol at a high product output with a minimized environmental footprint.
By partnering with us, you'll effectively enter the versatile market of e-methanol — whether it's used as a clean fuel or an energy vector/carrier in the chemical industry.
As a solution provider, we utilize proprietary technology, in-house core components and expert integration engineering, allowing us to offer performance guarantees for entire plants.
Our excellence in integration engineering ensures optimized initial investments and ongoing operational costs without compromising quality, safety or performance.
Our long-term service agreements (LTSA) emphasize operation and maintenance services through digital solutions. Our Metris platform enhances plant performance management, predictive maintenance, and autonomous operations, ensuring the production targets are met.

"The demand for renewable fuels is growing stronger and stronger as regulation comes in. It's time to drive innovation, reduce carbon emissions, and shape a brighter future through the revolutionary potential of different e-fuels. Take the first step towards a better tomorrow — start your sustainable journey with us today."
Henrik Grönqvist
Global Director, e-Methanol, ANDRITZ
With extensive experience in building pulp mills we provide scalable solutions around biogenic CO₂ and renewable fuels. Accessing over 200 MTA of biogenic CO2 through our delivered pulp mills, ANDRITZ can deliver unique integration solutions and synergy benefits by linking the e-fuel production with the pulp mill process.
Finnish forest industry company Metsä Group has already entered into a cooperation with ANDRITZ to explore the integration of carbon capture into a bioproduct mill.
We offer integrated P2X solutions for the production of e-methanol, taking responsibility for delivering and integrating the technologies. The standardized and modularized islands include green hydrogen, carbon capture, and methanol synthesis. Our plants are tailored to the customer's needs and site-specific conditions.
ANDRITZ's holistic solutions include
As a global company with industry-leading technologies, we provide full performance guarantees and life-cycle services for the e-methanol plants and, as a trusted partner, make your project safe. Our widely distributed manufacturing and service centers offer responsive and reliable local support and resources.
We provide complete EPC solutions with guarantees and long-term service agreements, addressing all your needs efficiently and cohesively.
Nobody can do it alone —together, we tackle today's challenges with precise and responsive communication.
With a presence in 280 locations worldwide, we can efficiently build P2X solutions wherever you want to build the plant.
As a stable, global company with over 170 years of history, we secure your green transition investment far into the future. Furthermore, ANDRITZ is a trusted partner that provides performance guarantees for the P2X plants based on measured feedstock and production output.

