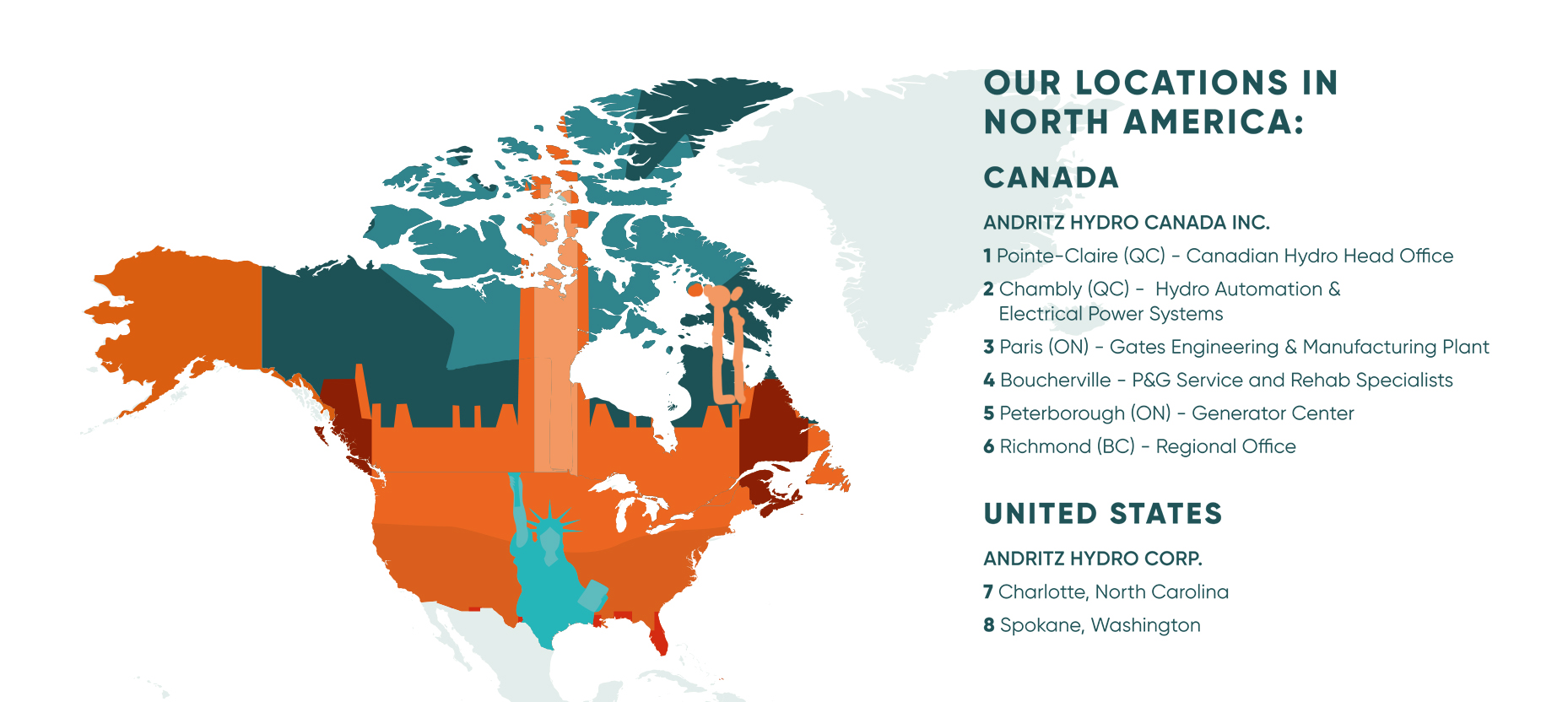
North America
Hydropower installed capacity: | 185 GW | |
Generation by hydropower: | 654 TWh | |
Capacity added: | 1,108 MW | |
Pumped storage installed capacity: | 22 GW | |
Pumped storage capacity added: | 96 MW | |
|
Countries: 2
Canada, The United States
Population: 372.22 Million
Hydropower installed capacity: | 185 GW | |
Generation by hydropower: | 654 TWh | |
Capacity added: | 1,108 MW | |
Pumped storage installed capacity: | 22 GW | |
Pumped storage capacity added: | 96 MW | |
|
The wealth of natural resources in continental North America makes it ideal for generating renewable energy. Hydropower has been a major contributor to the electricity market for many years and is still essential for supplying electricity to millions of people. The North American hydropower sector has seen positive growth in recent years, driven by regulatory approaches that will further maximize the potential for hydropower development and modernization.
Canada, which has abundant water resources, is thought to have an unexploited technical hydropower potential of 163 GW, while the United States has a remaining technically feasible capacity of about 150 GW. Across the continent, 1 GW of new hydropower capacity came online in 2022.
The relationship between hydropower and indigenous communities in North America is crucial to ensure we meet our energy needs while ensuring the communities play an active role in the acceptance and development of projects on their native lands.
Some government owned utilities have announced reconciliation action plans to ensure proactive engagement and involvement of indigenous communities. Collaborative efforts will be required between governments, industry, and indigenous groups to ensure a sustainable future in North America.
Furthermore, stringent measures are being implemented to protect fish populations, ensuring minimal disruption to aquatic ecosystems. The push toward sustainability in North American hydropower also favors ongoing modernization efforts. Aging infrastructure is being upgraded to enhance efficiency, safety, and environmental friendliness. Moreover, there's a growing emphasis on incorporating technological innovation to optimize operations and minimize any ecological impacts. One notable advance lies in the expansion of pumped storage facilities. They enable excess energy to be stored during periods of low demand and released during peak hours, thereby enhancing grid stability and power supply security.
