Input
- Fridges and freezers with CFC/pentane
A particular benefit is that even modern refrigerators – in which the insulation materials have been expanded using highly-explosive pentane gas – can be processed at the same time as CFC appliances without a risk of fire.
Fridge recycling system ANDRITZ - BORSIG
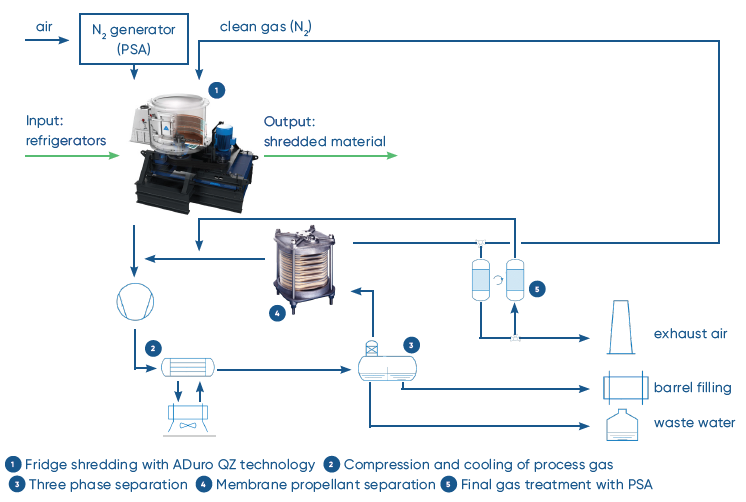
The completely sealed system of the ADuro QZ shredder takes in the refrigerators in batches and separates them in their individual components. A subsequent matrix degassing extracts the CFC from the insulating foam. With this gentle and environmentally friendly method of processing, the ANDRITZ recycling plants for refrigerators comply with highest European environmental standards. The extracted individual fractions of iron, copper, aluminum, plastics and polyurethane foam can directly be returned in the economic cycle.
Recycling plant for refrigerators
Matrix degassing unit
When it is introduced into the PMR process unit, the process gas is directed to an oil-injected screw-type compression system that is operated at a discharge pressure of approx. 12 bar(a). The gas/vapor is routed to the condensation skid and cooled down to 10-15 °C, which liquifies a significant portion of propellant and water. The condensate is fed into a decanter, from where the aqueous phase is routed to a waste water collector tank and the propellant to a barrel-filling station. Residual, noncondensable gas (mainly Nitrogen) / vapor (propellant) portion is fed to the membrane stage. Driven by a partial pressure difference, the propellant is passing the membrane, while the Nitrogen remains on the upper side. This permeated gas is routed to the inlet of gas compressor.
Consequently, this recirculation raises. During shredding, the propellants are released to the system’s gas phase. To maintain a non-hazardous atmosphere, Nitrogen is introduced as an inert gas. The corresponding gas mixture needs to be treated prior to exposure to the atmosphere. the dew point of propellant for efficient liquification during cooling in main condenser.
On the membrane’s upstream outlet, pre-cleaned residual exhaust gas can be partially returned to the shredder. Another portion is routed to activated carbon type pressure swing adsorption (PSA) for final purification before venting to the environment. In the PSA unit, one adsorber vessel is in operation for removing residual HC traces, whereas the second installed adsorber is in regeneration under low pressure returning the captured propellant to compressor suction. Both adsorbers are connected to a changeover valve combination, allowing operation / regeneration in a defined time cycle. The cooling is achieved by a free air-cooled system combined with a chiller unit, using a closed loop.
ANDRITZ-BORSIG PMR

ATN Engineering is recognized as an innovator in the recycling sector with its unique drill head system, which enables the safe and efficient removal of hazardous oil and gas from end-of-life refrigerators. The company also supplies feeding logistics and equipment for the recycling of industrial coolers, air conditioning equipment, and heat pumps. ATN provides engineering, manufacturing, installation, commissioning and servicing of recycling equipment. To date, the company has delivered more than 200 degassing units worldwide.
Inside the compressor and the connected pipework, a pressure of more than 6 bar is possible, depending on the ambient temperature and the type of gas. In general, there are no draining valves in the cooling system of a domestic fridge. Therefore, a connection to the pressurized system must be made before draining is possible. This connection has to be made without losing any gas during this operation. The aspect of flammable gases must also be considered.
A cooling circuit consists of oil and a gas (refrigerant). It is very important to first drain the oil because the pressure of the gas will help push it out. This can only be done by making a hole at the lowest point of the oil.
The hole should be large enough to drain the oil as quickly as possible but not so fast that the gas breaks through the oil surface. In this case, the pressure of the gas cannot be used to push the oil out. As a result, oil will remain inside the compressor.
Once the gas is removed and the system is vacuumed, it is no longer possible to remove the oil. Therefore it is important to drain underneath the oil to make sure all the oil will be drained. After the oil is drained, the gas is evacuated until there is no longer any pressure in the compressor. No pressure means -1 bar relative to the ambient pressure.





